Navigation:
Orient: Using the Display : Orient versions to 4.8
The Orient program can be used to create 3D maps of energies or other quantities mapped onto a surface. These can be scalar or vector maps. Here we will look into using scalar maps.
The idea is to create something that looks like this: 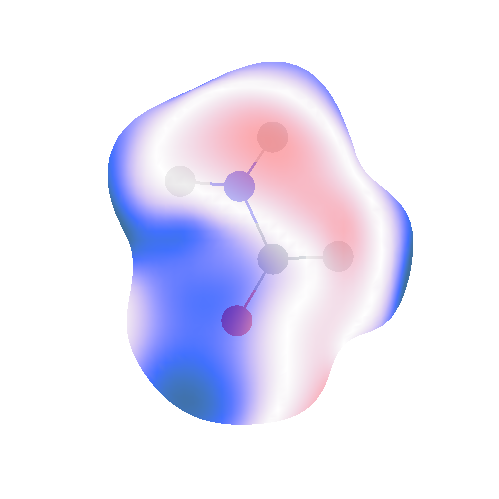 In this map, I have visualised the difference in the electrostatic potential arising from a rank 0 (charge only) multipole model (from the ISA) against a reference potential from SAPT(DFT). Actually, rather than calculate a potential, I have calculated the electrostatic energy between either the charge model or actual density of formamide and a unit point charge. This point charge has been placed at various points on a 0.001 a.u. isodensity surface. Orient allows us to visualise the errors made by the point charge model. This is only one view of an image that can be rotated/moved around using a mouse.
In this map, I have visualised the difference in the electrostatic potential arising from a rank 0 (charge only) multipole model (from the ISA) against a reference potential from SAPT(DFT). Actually, rather than calculate a potential, I have calculated the electrostatic energy between either the charge model or actual density of formamide and a unit point charge. This point charge has been placed at various points on a 0.001 a.u. isodensity surface. Orient allows us to visualise the errors made by the point charge model. This is only one view of an image that can be rotated/moved around using a mouse.
Consider what we need to make such an image:
- molecular geometry
- multipole model
- reference energies/potential
- surface map (triangulated)
- Orient input file for the display
We will usually have the first two so let's consider the others here.
Generating the display data using CamCASP
The CamCASP program can be used to generate an isodensity surface using the Display module. And then the ENERGY-SCAN module can be used to calculate the reference energies for this surface. ajm:camcasp:energy-scan-display
Orient input file for display
Let's start with the Orient file for display as its requirements will become clearer once you see it. The input files used below have been created from an Orient display file generated using the Cluster program.
Display pre-computed reference energies
Here's the input file for displaying a reference energy already calculated, in this case, using the DISPLAY and ENERGY-SCAN modules in CamCASP: <code | formamide-display-reference.ornt> ! ORIENT display commands
UNITS BOHR
Parameters
- Sites 13 polarizable 11 S-functions 50000 Alphas 50000 Parameter-sets 50000 Pairs 100000
End
Types
- C Z 6 O Z 8 N Z 7 H1 Z 1 H2 Z 1 H3 Z 1
End
Molecule formamide at 0.0 0.0 0.0
- ! Units BOHR C 0.73690219 -0.29016270 0.00000000 Type C O -0.41965533 -2.26421099 0.00000000 Type O N -0.33761508 2.03824113 0.00000000 Type N H1 2.82092994 -0.20596490 0.00000000 Type H1 H2 -2.23332780 2.19617606 0.00000000 Type H2 H3 0.72278745 3.61139057 0.00000000 Type H3 ! #include HCONH2_DMA2_L4.mom
End Edit formamide
- ! #include formamide.axes Bonds Auto
End
Units Bohr kJ/mol
! This is a probe of the induction energy Atom X at 0.0 0.0 0.0 rank 0
- Q00 = 1.0
End
Display energy
- Title "formamide...Q 1.0 elst " Molecule formamide ! * Use the Compare line for energy comparisons and ! * comment out the Radii, Step and Grid lines ! Compare with energy_values.dat Import formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst with values ! Radii scale 2.0 ! Step 0.75 B ! Grid exp Colour-map
- 0 210 0.25 1 6 240 0.75 1
- 12 300 1.0 0 18 360 0.75 1 24 390 0.25 1
End
Finish </code> Points to note:
- No multipoles included because...
...we import a grid file that contains the electrostatic energies calculated using the ENERGY-SCAN module in CamCASP.
Also, we have commented out the lines in Display energy that calculate a grid using the atomic van der Waals radii. Once again, this is because the grid is included in the file we imported.
The import from file formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst is done with values. This tells Orient to import energy values at each point.
In this calculation, the probe molecule X does nothing.
You need to adjust the Viewport (distance at which you are viewing the molecule) and Colour-Scale to something appropriate.
Run this using Orient compiled with OPEN_GL and you will see something like this:
The Orient output should look like this: <code> $ orient < HCONH2_display.ornt
- ORIENT version 4.8.15 29 May 2014
- by
- Anthony Stone
...
Molecule 1 (Site 1): formamide Origin position (cartesian) 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000
Site 2: C Type C Position (cartesian) 0.73690 -0.29016 0.00000
...
Preparing display: formamide...Q 1.0 elst Importing grid and values from file formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst 4704 points and 9404 triangles read from file formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst Displaying values read from file formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst Minimum energy = -174.19700 kJ/mol Maximum energy = 204.53000 kJ/mol Colour scale:
- bottom -200.00000 kJ/mol top 200.00000 kJ/mol
4704 points, 9404 triangles
</code> The code prints out the Minimum and Maximum energies encountered. Use these values to set the range of the energy scale using the Colour-scale command.
Display using van der Waals surfaces
It is also possible to generate a display within Orient, using the van der Waals surfaces for each atom to create a molecular surface. Orient has default radii for each atom, but they can be set manually (see the Orient manual). Here we use the standard radii. Here's the input file: <code | formamide-display-vdWsurface.ornt> ! ORIENT display commands
UNITS BOHR
Parameters
- Sites 13 polarizable 11 S-functions 50000 Alphas 50000 Parameter-sets 50000 Pairs 100000
End
Types
- C Z 6 O Z 8 N Z 7 H1 Z 1 H2 Z 1 H3 Z 1
End
Molecule formamide at 0.0 0.0 0.0
- #include formamide_aQZ_B+DF_z0.1_aQZset2_L4.mom
End Edit formamide
- ! #include formamide.axes Bonds Auto
End
Units Bohr kJ/mol
! This is a probe of the induction energy Atom X at 0.0 0.0 0.0 rank 0
- Q00 = 1.0
End
Display energy
- Title "formamide...Q 1.0 elst " Molecule formamide ! * Use the Compare line for energy comparisons and ! * comment out the Radii, Step and Grid lines ! Compare with energy_values.dat ! Import formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst with values Radii scale 1.5 Step 0.75 B Grid exp Colour-map
- 0 210 0.25 1 6 240 0.75 1
- 12 300 1.0 0 18 360 0.75 1 24 390 0.25 1
End
Finish </code> Points to note:
We now need a multipole moment file. I've used an ISA calculation and the multipole moments can be found in formamide_aQZ_B+DF_z0.1_aQZset2_L4.mom.
The surface is a 1.5 x vdW surface. The 1.5 is set using the Radii command.
Step 0.75 B sets the quality of the surface by defining the size of the triangle edges, in this case, in Bohr.
Grid Exp defines the kind of grid. See the Orient manual for details.
- This time the range of energies is smaller as we have no penentration contribution in this calculation.
- Also, the shape of the surface is quite different from the 0.001 a.u. isodensity surface shown above.
Difference maps using Orient
Now we know how to display energies, but what about differences in energies? We often want to compare two models: say, the rank 0 multipole model may need to be compared with SAPT(DFT) or, perhaps more appropriately, with a rank 4 model. How to we do this?
The idea here is to import a grid with values (as we did with the SAPT(DFT) reference above) and use it as a REFERENCE. We then compare the energies calculated with a model against these values. Orient will plot the difference. Here's an input file for a comparison against pre-computed SAPT(DFT) electrostatic energies: <code | formamide-compare-against-sapt.ornt> ! ORIENT display commands
UNITS BOHR
Parameters
- Sites 10 polarizable 8 S-functions 50000 Alphas 50000 Parameter-sets 50000 Pairs 100000
End
Types
- C Z 6 O Z 8 N Z 7 H1 Z 1 H2 Z 1 H3 Z 1
End
Molecule HCONH2 at 0.0 0.0 0.0
- #include formamide_aQZ_B+DF_z0.1_aQZset2_L4.mom
End Edit HCONH2
- Bonds Auto Limit Rank 0 for sites C O N Limit Rank 0 for sites H1 H2 H3
End
Units Bohr kJ/mol
! This is a probe of the induction energy Atom X at 0.0 0.0 0.0 rank 0
- Q00 = +1.0
End
Display energy
- Title "HCONH2...Q 1.0 Elst " Molecule HCONH2 ! * Use the Compare line for energy comparisons and ! * comment out the Radii, Step and Grid lines Import formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst Reference
! Radii scale 2.0 ! Step 0.75 B ! Grid exp
- Colour-map
- 0 210 0.25 1 6 240 0.75 1
- 12 300 1.0 0 18 360 0.75 1 24 390 0.25 1
End
Finish </code> Points to note:
- We need a multipole model.
We have used the LIMIT option to reduce the rank of the model, in this case, from rank 4 on all atoms, to rank 0 on the hydrogen atoms and rank 0 on the heavier atoms. You could make any model truncation you need.
Import the reference values using Import formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst Reference. The Reference command tells Orient that everything will be compared against the energies in this file.
The Radii, Step and Grid commands are commented out as the Import command reads the grid along with the reference values.
- Since we will be displaying differences, reduce the energy scale.
As usual, Orient will print out a summary when you run it. Here's the tail end of the output containing the relevant details: <code> Preparing display: HCONH2...Q 1.0 Elst Importing grid and values from file formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst 4704 points and 9404 triangles read from file formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst Displaying calculated values Maximum difference = 14.13234 kJ/mol Minimum difference = -39.17835 kJ/mol r.m.s. difference = 14.57066 kJ/mol average difference = -7.47084 kJ/mol Standard deviation = 12.51095 kJ/mol Colour scale:
- bottom -30.00000 kJ/mol top 30.00000 kJ/mol
4704 points, 9404 triangles </code> The max and min differences are reported and may be used to determine the energy diference scale needed. Additionally Orient prints out the r.m.s. and average differences.
Differences against references calculated with Orient
What if we want to compare a rank 0 multipole model against a rank 4 model? Or the DMA multipoles against the ISA multipoles? In these cases, we might want to define a reference using the ISA rank 4 multipoles. Once we have this reference, we could use the above method to compare any other multipole model against the reference.
Define the reference
We first need to define a grid. It could be an isodensity grid, or we may use the Orient program to create a van der Waals grid. For the former use <code> Display energy
- Title "HCONH2...Q 1.0 Elst " Molecule HCONH2 Import formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst no values
- ..
End </code> Notice the Import ... no values command. We want the grid only, not the energy values in the grid file.
For the internally generated, van der Waals grid, use <code> Display energy
- Title "HCONH2...Q 1.0 Elst " Molecule HCONH2 Radii scale 1.5 Step 0.75 B Grid exp
- ..
End </code> This is exactly what we used before.
But what about the reference ISA rank 4 energies? To get these, we need to define the model, set the rank (if necessary), and then Orient will use it to calculate the energies at all grid points: <code> Molecule HCONH2 at 0.0 0.0 0.0
- #include formamide_aQZ_B+DF_z0.1_aQZset2_L4.mom
End Edit HCONH2
- Bonds Auto Limit Rank 4 for sites C O N Limit Rank 4 for sites H1 H2 H3
End </code>
The last step is to write out the grid and these reference energies to file. This is done using the Write command in the Display energy module, like so (for the 1.5 vdW surface generated with Orient): <code> Display energy
- Title "HCONH2...Q 1.0 Elst " Molecule HCONH2 Radii scale 1.5 Step 0.75 B Grid exp Colour-map
- 0 210 0.25 1 6 240 0.75 1
- 12 300 1.0 0 18 360 0.75 1 24 390 0.25 1
Write HCONH2_1.5vdW_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid with values
End </code> Of course, this could have been done with the 0.001 isosurface too. These commands would look like: <code | formamide-generate-reference-isosurface.ornt> Display energy
- Title "HCONH2...Q 1.0 Elst " Molecule HCONH2 Import formamide_1.00E-03_iso_aQZ_Q.elst no values Colour-map
- 0 210 0.25 1 6 240 0.75 1
- 12 300 1.0 0 18 360 0.75 1 24 390 0.25 1
Write HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid with values
End </code> Now the grid and values will be in file HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4.grid
Here's the full Orient command file for the latter case.
Now we've got the reference surface and energies in the file HCONH2_1.5vdW_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid or HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid.
Making the difference map
As before, we use the calculated reference files to make difference maps. For example, the full Orient input file for the HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid reference is: <code> ! ORIENT display commands
UNITS BOHR
Parameters
- Sites 10 polarizable 8 S-functions 50000 Alphas 50000 Parameter-sets 50000 Pairs 100000
End
Types
- C Z 6 O Z 8 N Z 7 H1 Z 1 H2 Z 1 H3 Z 1
End
Molecule HCONH2 at 0.0 0.0 0.0
- #include formamide_aQZ_B+DF_z0.1_aQZset2_L4.mom
End Edit HCONH2
- Bonds Auto Limit Rank 0 for sites C O N Limit Rank 0 for sites H1 H2 H3
End
Units Bohr kJ/mol
Atom X at 0.0 0.0 0.0 rank 0
- Q00 = +1.0
End
Display energy
- Title "HCONH2...Q 1.0 Elst " Molecule HCONH2
Import HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid Reference Colour-map
- 0 210 0.25 1 6 240 0.75 1
- 12 300 1.0 0 18 360 0.75 1 24 390 0.25 1
End
Finish </code> In this example we compare the ISA rank 0 model against the reference ISA rank 4 model on the 0.001 a.u. isosurface. No more figures, but here are summaries of the outputs for various ranks:
Rank 4
This one is our test: it should have no errors as this model was used to create the reference: <code> Preparing display: formamide...Q 1.0 elst Importing grid and values from file HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid 4704 points and 9404 triangles read from file HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid Displaying calculated values Maximum difference = 0.00001 kJ/mol Minimum difference = -0.00001 kJ/mol r.m.s. difference = 0.00000 kJ/mol average difference = -0.00000 kJ/mol Standard deviation = 0.00000 kJ/mol Colour scale:
- bottom -30.00000 kJ/mol top 30.00000 kJ/mol
4704 points, 9404 triangles </code>
Rank 3
<code> 4704 points and 9404 triangles read from file HCONH2_0.001iso_ISA_L4L4_ref.grid Displaying calculated values Maximum difference = 7.25748 kJ/mol Minimum difference = -4.39074 kJ/mol r.m.s. difference = 1.55204 kJ/mol average difference = 0.03929 kJ/mol Standard deviation = 1.55171 kJ/mol </code> Errors are larger.
Rank 0
<code> Maximum difference = 26.63755 kJ/mol Minimum difference = -25.66614 kJ/mol r.m.s. difference = 12.73403 kJ/mol average difference = 0.68858 kJ/mol Standard deviation = 12.71675 kJ/mol </code> Errors are much larger.
