Contents
Literature
Read this in order:
New representation for the dispersion by Hodges and Stone (Molecular Physics vol 98). Important paper. Read fully. Make extensive notes.
Distributed Dispersion by Williams and Stone Read the Introduction and get an idea of the problem
Distributed Dispersion by Misquitta and Stone The dispersion models you are using have been obtained using the methods in this paper. Read carefully and make extensive notes. In this paper, I state that the dispersion model should match the total dispersion energy defined as $E^{(2)}_{\rm DISP} = E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,pol} + E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,exch}$, but other groups suggest that we should use only the first term in that sum, the polarization term ('pol').
Here are some papers by Dobson on problems with the dispersion expansion you are using:
Dispersion: Is there a problem by Dobson (Aust. J. Chem. 54)
Beyond the pair-wise approximation by Dobson (Int. J. Quant. Chem. 114)
Dispersion Models
Before reading this, make sure you fully understand the structure of an Orient input file as described in the tutorial on Orient Energy calculations.
Here we will explore some examples of dispersion energy calculations with Orient. This tutorial is currently a subset of the more general one on energy calculations, and is meant for research students.
Pyridine dimer
The goal here is to investigate various dispersion models for pyridine. The isotropic dispersion coefficients have been calculated using the WSM procedure with PBE0/AC and the ALDA+CHF kernel with a d-aug-cc-pVTZ basis set. The full dispersion model is on a separate page.
Here's the Orient command file for this calculation. Follow the instructions on that page to set up this file properly.
Double-H-bonded geometry (Hb1)
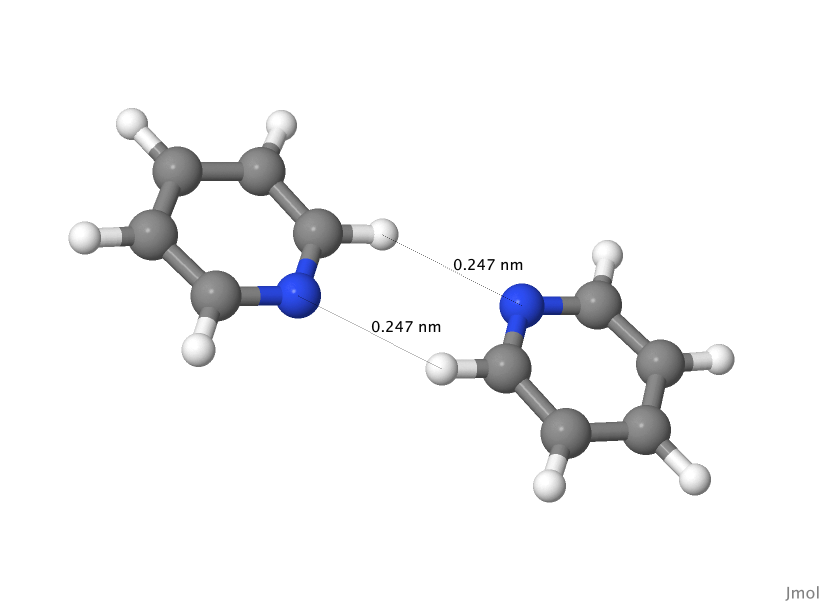
You will need a pyridine dimer geometry file to perform a calculation. As explained on the Orient: Energy Calculations page, the dimer geometry file contains information needed to construct the dimer complex from two monomers. Here's the pyridine dimer geometry file you will use now. Save this in file //pyr2.geom//.
pyridine dimer geometry: Double-H-Bonded
! Configs read from file : Min-1-Hb1.geom
! Minimum 12, energy = -16.148904 KJ/MOL
! R-scalings 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 1.05 1.10 1.20 1.40
! UNITS BOHR DEGREE KJ/MOL
1 -4.62746800 7.42808480 -0.00000080 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
2 -4.91668475 7.89234010 -0.00000085 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
3 -5.20590150 8.35659540 -0.00000090 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
4 -5.49511825 8.82085070 -0.00000095 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
5 -5.78433500 9.28510600 -0.00000100 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
6 -6.07355175 9.74936130 -0.00000105 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
7 -6.36276850 10.21361660 -0.00000110 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
8 -6.94120200 11.14212720 -0.00000120 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000
9 -8.09806900 12.99914840 -0.00000140 179.99990900 -0.00000100 -0.00000200 -1.00000000Important
The format of this file is as follows:
- Comments are indicated by the initial '! ' followed by a space.
- Data lines are: Index Rx Ry Rz alpha Nx Ny Nz
Here ${\mathbf R} = (R_x,R_y,R_z)$ is the position vector of the centre of the molecule...
...which is rotated by $\alpha$ about the axis defined by the unit vector ${\mathbf N} = (N_x,N_y,N_z)$.
- The units used are set in the Orient command file. We will normally define lengths in Bohr and angles in Degrees.
Now run Orient. If all goes well and nothing is missing, you will get an output which will end with:
...
...
Energy calculation
Rx Ry Rz alpha Nx Ny Nz Index disp
1.00000 -4.62747 7.42808 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.1086983E+03
2.00000 -4.91668 7.89234 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.6508604E+02
3.00000 -5.20590 8.35660 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.3905442E+02
4.00000 -5.49512 8.82085 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.2366363E+02
5.00000 -5.78433 9.28511 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.1456060E+02
6.00000 -6.07355 9.74936 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.9136092E+01
7.00000 -6.36277 10.21362 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.5862099E+01
8.00000 -6.94120 11.14213 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.2595136E+01
9.00000 -8.09807 12.99915 -0.00000 179.99991 -0.00000 -0.00000 -1.00000 -0.6722668E+00
Finished at 15:35:43 on 26 Nov 2015 The dispersion energies are in the last column in the current energy units of kJ/mol.
Important
The Orient output is long but if all goes well (i.e., if there are no errors) then all you need is this last block that contains the energies. The format of the block is determined by the line after 'Energy Calculation'. Here we should have data presented in the order
- Rx Ry Rz alpha Nx Ny Nz Index disp
but this is not quite right as the 'Index' column actually appears first, so the actual order is
- Index Rx Ry Rz alpha Nx Ny Nz disp
The reference dispersion energies are obtained from a SAPT(DFT) calculation of the interaction energy using the PBE0/AC density functional, the ALDA+CHF response kernel, and the Sadlej-pVTZ MC+ basis set. In SAPT(DFT), the dispersion energy is split into two parts called $E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,pol}$ and $E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,exch}$. I have calculated these energies and they are present in the following file. The first term is under the column titled //disp// and the second under //exdisp//. So you get the total dispersion energy by summing up the energies in columns //disp// and //exdisp// in this file:
Reference interaction energies for double-H-bonded dimers
kJ/mol Rx Ry Rz elst exch ind exind disp exdisp dHF total pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_1 -4.62746800 7.42808480 -0.00000080 -391.78298 906.47847 -466.78920 301.55526 -148.53278 29.19456 63.91539 294.03872 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_2 -4.91668475 7.89234010 -0.00000085 -175.41151 394.79266 -158.07765 115.88891 -85.47441 18.05324 -15.29883 94.47239 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_3 -5.20590150 8.35659540 -0.00000090 -79.80775 161.29153 -55.08349 40.44190 -49.60674 9.47369 -12.97352 13.73563 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_4 -5.49511825 8.82085070 -0.00000095 -38.49000 63.64067 -20.28133 13.62851 -29.14987 4.52402 -5.82393 -11.95193 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_5 -5.78433500 9.28510600 -0.00000100 -20.13901 24.66869 -8.04327 4.54295 -17.44163 2.03467 -2.24451 -16.62210 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_6 -6.07355175 9.74936130 -0.00000105 -11.55184 9.49641 -3.49405 1.52050 -10.66386 0.87805 -0.81570 -14.63049 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_7 -6.36276850 10.21361660 -0.00000110 -7.20094 3.64456 -1.68429 0.51856 -6.68995 0.36815 -0.28800 -11.33191 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_8 -6.94120200 11.14212720 -0.00000120 -3.32496 0.52344 -0.52194 0.06584 -2.87627 0.06109 -0.03432 -6.10712 pyr2-Min-1-Hb1_9 -8.09806900 12.99914840 -0.00000140 -0.94653 0.00461 -0.10704 0.00159 -0.74583 0.00163 -0.00015 -1.79172
Here too the units are kJ/mol.
Important
To find our more about intermolecular interactions see the pages on Topics in Intermolecular Interactions. These topics are not complete, but include information about the dispersion energy.
Important
Compare these two sets of dispersion energies graphically. It will be best to plot the dispersion energy from the model (Orient output) and the reference SAPT(DFT) calculation (sum of 'disp' and 'exdisp') against $R$, the centre-of-mass separation of the two molecules.
Use Gnuplot or Excel for this. As usual with any plot, make sure you choose a good range for the x/y-axes, use axis labels, and make sure you have an intelligible legend.
You may also plot the % error against $R$.
Stacked geometry: S1
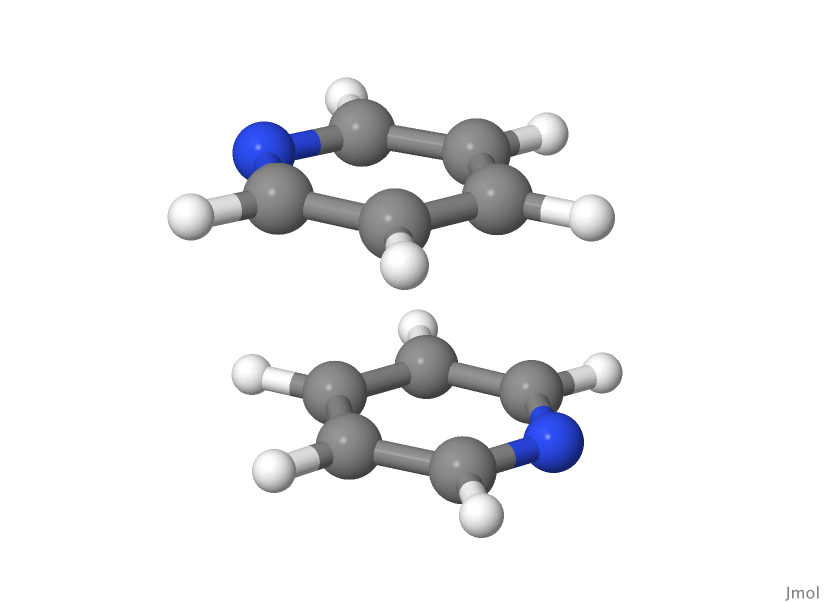
Here the dispersion interaction is quite strong as the molecules are nearly planar and the $\pi$-electron clouds on the two pyridine molecules interact quite strongly.
The dimer geometry file for this dimer configuration is:
Pyridine dimer stacked S1 geometry
! Configs read from file : Min-2-S1.geom
! Minimum 4, energy = -15.865773 KJ/MOL
! R-scalings 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 1.05 1.10 1.20 1.40
! UNITS BOHR DEGREE KJ/MOL
1 -1.79942320 -0.73612400 5.12911280 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
2 -1.91188715 -0.78213175 5.44968235 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
3 -2.02435110 -0.82813950 5.77025190 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
4 -2.13681505 -0.87414725 6.09082145 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
5 -2.24927900 -0.92015500 6.41139100 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
6 -2.36174295 -0.96616275 6.73196055 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
7 -2.47420690 -1.01217050 7.05253010 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
8 -2.69913480 -1.10418600 7.69366920 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000
9 -3.14899060 -1.28821700 8.97594740 180.00021200 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000And the reference SAPT(DFT) interaction energies and components are:
Pyridine dimer stacked S1 : SAPT(DFT)
kJ/mol elst exch ind exind disp exdisp dHF total pyr2-Min-2-S1_1 -93.68418 229.84666 -121.97931 117.41444 -104.53125 20.49225 -9.55649 38.00211 pyr2-Min-2-S1_2 -55.89101 137.13609 -67.86848 65.93106 -77.65630 13.50502 -8.40315 6.75323 pyr2-Min-2-S1_3 -33.41670 81.23861 -37.90498 36.83166 -57.86743 8.74817 -5.96320 -8.33387 pyr2-Min-2-S1_4 -20.05835 47.83876 -21.26223 20.50059 -43.28651 5.58199 -3.86950 -14.55525 pyr2-Min-2-S1_5 -12.14874 28.04879 -11.98552 11.36883 -32.53668 3.51790 -2.39791 -16.13334 pyr2-Min-2-S1_6 -7.48464 16.38945 -6.80518 6.28065 -24.59408 2.19461 -1.44595 -15.46515 pyr2-Min-2-S1_7 -4.74532 9.54668 -3.90642 3.45575 -18.70491 1.35737 -0.85578 -13.85263 pyr2-Min-2-S1_8 -2.20207 3.21641 -1.36632 1.04099 -11.05719 0.51030 -0.29046 -10.14833 pyr2-Min-2-S1_9 -0.98400 0.35555 -0.25850 0.09980 -4.24321 0.06907 -0.03340 -4.99470
As before, the dispersion energy is obtained by summing up the energies in columns //disp// and //exdisp//.
Important
Perform the same analysis of the dispersion energy for this and other dimer orientations.
Stacked S2 geometry
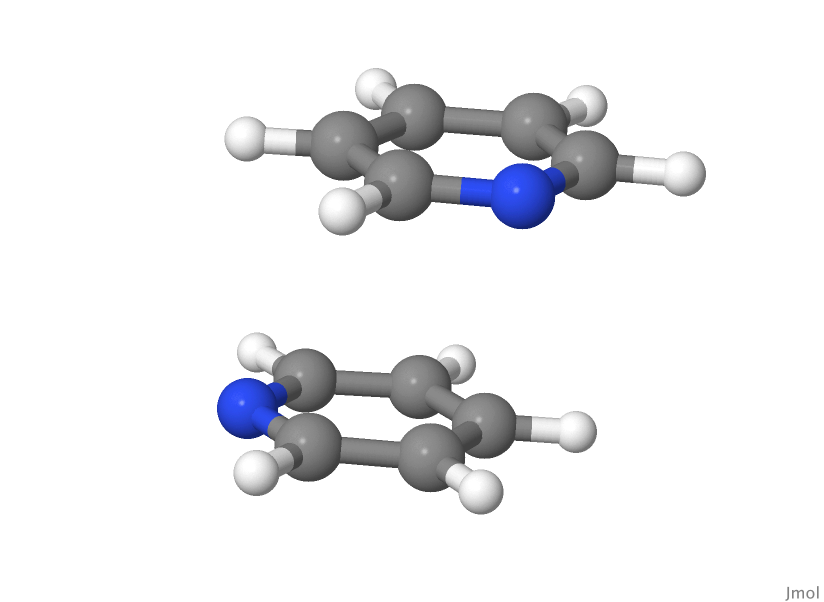
! Configs read from file : Min-3-S2.geom
! Minimum 21, energy = -15.415471 KJ/MOL
! R-scalings 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 1.05 1.10 1.20 1.40
! UNITS BOHR DEGREE KJ/MOL
1 -1.08088960 -1.19861520 5.19152480 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
2 -1.14844520 -1.27352865 5.51599510 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
3 -1.21600080 -1.34844210 5.84046540 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
4 -1.28355640 -1.42335555 6.16493570 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
5 -1.35111200 -1.49826900 6.48940600 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
6 -1.41866760 -1.57318245 6.81387630 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
7 -1.48622320 -1.64809590 7.13834660 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
8 -1.62133440 -1.79792280 7.78728720 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400
9 -1.89155680 -2.09757660 9.08516840 179.99987000 0.82854802 -0.55821602 0.04362400Stacked S2 SAPT(DFT) interaction energies
kJ/mol elst exch ind exind disp exdisp dHF total pyr2-Min-3-S2_1 -94.36569 233.64001 -124.91985 120.20669 -104.48047 20.52825 -8.85141 41.75753 pyr2-Min-3-S2_2 -55.91630 139.27155 -69.16488 67.20437 -77.58576 13.53039 -8.26838 9.07098 pyr2-Min-3-S2_3 -33.13793 82.43018 -38.46427 37.39061 -57.80902 8.76312 -6.01039 -6.83769 pyr2-Min-3-S2_4 -19.65599 48.50345 -21.47742 20.71520 -43.25229 5.58866 -3.95289 -13.53129 pyr2-Min-3-S2_5 -11.70362 28.41093 -12.05830 11.43750 -32.52121 3.51777 -2.47057 -15.38751 pyr2-Min-3-S2_6 -7.03240 16.58333 -6.81682 6.28864 -24.59363 2.19060 -1.49815 -14.87843 pyr2-Min-3-S2_7 -4.30614 9.65228 -3.89611 3.44323 -18.72228 1.35250 -0.88994 -13.36646 pyr2-Min-3-S2_8 -1.80769 3.24548 -1.35061 1.02494 -11.08604 0.50547 -0.30197 -9.77042 pyr2-Min-3-S2_9 -0.67850 0.35748 -0.25399 0.09493 -4.27776 0.06758 -0.03315 -4.72341
T1 geometry
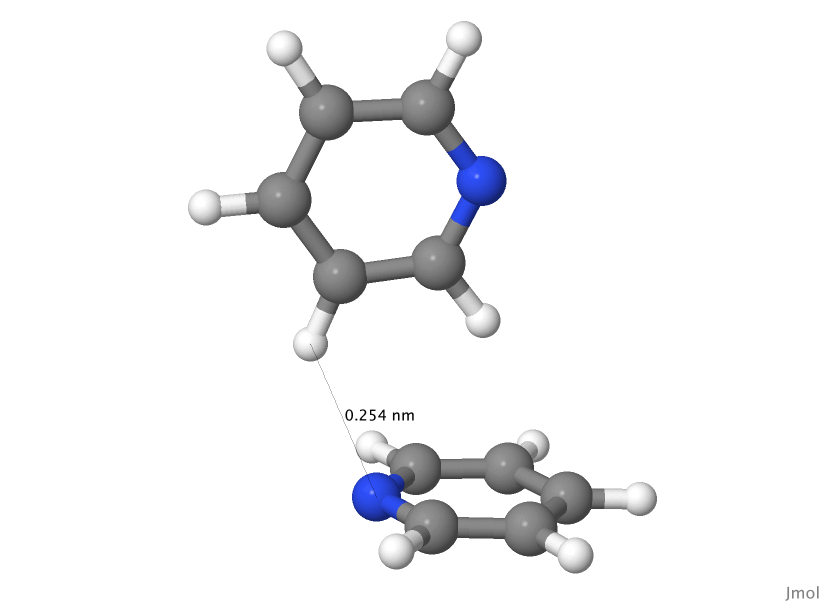
! Configs read from file : Min-4-T1.geom
! Minimum 6, energy = -14.741407 KJ/MOL
! R-scalings 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 1.05 1.10 1.20 1.40
! UNITS BOHR DEGREE KJ/MOL
1 -0.00118960 2.23630400 6.94015440 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
2 -0.00126395 2.37607300 7.37391405 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
3 -0.00133830 2.51584200 7.80767370 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
4 -0.00141265 2.65561100 8.24143335 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
5 -0.00148700 2.79538000 8.67519300 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
6 -0.00156135 2.93514900 9.10895265 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
7 -0.00163570 3.07491800 9.54271230 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
8 -0.00178440 3.35445600 10.41023160 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288
9 -0.00208180 3.91353200 12.14527020 184.79799900 -0.70659688 0.04176199 0.70638288T1 H-bonded dimer SAPT(DFT) energies
kJ/mol elst exch ind exind disp exdisp dHF total pyr2-Min-4-T1_1 -143.75060 365.78637 -163.67329 134.43732 -104.97735 20.27286 -1.54149 106.55382 pyr2-Min-4-T1_2 -73.22983 180.25459 -68.92160 59.48863 -68.93918 12.05092 -9.56961 31.13392 pyr2-Min-4-T1_3 -38.33338 86.66029 -29.49579 25.66332 -45.49253 6.75683 -6.56118 -0.80242 pyr2-Min-4-T1_4 -21.06549 40.98139 -12.90868 10.95067 -30.24904 3.63478 -3.51241 -12.16878 pyr2-Min-4-T1_5 -12.39565 19.17593 -5.82614 4.65623 -20.31555 1.89593 -1.72381 -14.53305 pyr2-Min-4-T1_6 -7.91592 8.92305 -2.74621 1.98005 -13.81631 0.96697 -0.81672 -13.42508 pyr2-Min-4-T1_7 -5.50328 4.14028 -1.37392 0.84514 -9.53385 0.48474 -0.38403 -11.32493 pyr2-Min-4-T1_8 -3.25632 0.88810 -0.43455 0.16035 -4.76954 0.11781 -0.08875 -7.38291 pyr2-Min-4-T1_9 -1.67809 0.03669 -0.09847 0.00715 -1.46121 0.00649 -0.00755 -3.19500
Random Geometry set
Use the set of random dimer geometries from here (This is a gzipped file. To open it, use gunzip (see below)) to compare dispersion energies from the dispersion models (using Orient) with dispersion energies from SAPT(DFT).
You will need to compare the model dispersion energies with those from SAPT(DFT) using a scatter plot. Keep the SAPT(DFT) reference energies on the $x$-axis.
Important
Gzip:
The Wiki will not allow me to include certain kinds of files, so I have used the gzip program to zip some files. These have the ending *.gz. To use them you first need to gunzip them as follows:
$ gunzip pyr2-saptdft-disp.dat.gz
This will result in the file
& pyr2-saptdft-disp.dat
You will be able to view this file as a standard text file.
The sISA dispersion model
So far you have been using a dispersion model with a single dispersion coefficient between all pairs of sites. All sites used damping parameter $\beta_{\rm disp} = 1.67$ a.u. This damping parameter was determined from the ionisation energies of the two interacting pyridine molecules (see the paper by Misquitta and Stone 2008 (Paper [3])). Now you will use a damping model in which every pair of sites has its own damping parameter. This model has been derived using the Iterated Stockholder Atoms algorithm (ISA) to partition the molecular density into atomic parts, and then the damping coefficients for every pair of the atomic parts has been determined using the density decay of the atomic parts.
Mathematical details to follow.
The damping model is contained in this file. You will need to modify the Orient command file to include this model. This can be done as follows:
The Orient command file with the simple dispersion model contains the lines:
Pairs ! We will use a damping model based on the Tang--Toennies incomplete Gamma function ! with damping parameter \beta = 1.67 a.u. Dispersion damping factor 1.67 ! And we will include the dispersion model that should be in file pyr2-disp.pot #include ./pyr2-disp.pot End
Modify this to be
Pairs ! We will use a damping model based on the Tang--Toennies incomplete Gamma function ! with damping parameter \beta = 1.67 a.u. #include ./pyr2-damp3-ab-sisa-0.80.disp ! And we will include the dispersion model that should be in file pyr2-disp.pot #include ./pyr2-disp.pot End
Here pyr2-damp3-ab-sisa-0.80.disp is the name of the file containing the dispersion damping model. Remember you need to gunzip it! Now run Orient as before.
Important
Tasks:
Use this dispersion model (call it damp3 to be consistent with my notation) to calculate the dispersion energies for the four pyridine dimer orientations you have already studied.
However, in addition to using as your reference the sum of SAPT(DFT) energies $E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,pol} + E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,exch}$ (this is what you have done before), also use just the first term. This seems to be required by some theoretical studies. So here we will ask the question: which of these energies does the model fit?
Finally use the set of random dimers to make two scatter plots with this dispersion damping model: one comparing the model to SAPT(DFT) energies $E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,pol} + E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,exch}$, and the other comparing to SAPT(DFT) energies $E^{(2)}_{\rm disp,pol}$.
